Phosphatidylcholine vs Phosphatidylserine: Which Phospholipid Is Right for You?
Authors:

Dr. Thomas Wnorowski
PhD, CNCC Research Director, BodyBio & Biomedical NutritionistPhosphatidylserine (PS) is a phospholipid you may have seen in nootropic formulas or biohacking circles for its brain-boosting reputation. Phosphatidylcholine (PC) is another major phospholipid that also supports brain function—along with liver, gut, and mitochondrial health.
So if you’re choosing to supplement, which one is better? As with most questions about how to best support your health, the answer is more nuanced than “either/or.” These two phospholipids work together at the cellular level. We need both for optimal membrane structure and signaling.
In this article, we’ll explore the properties, similarities, and differences between phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylserine, how they’re produced in the body, and how to best support both through supplementation and diet.
What’s the Difference Between Phosphatidylcholine and Phosphatidylserine?
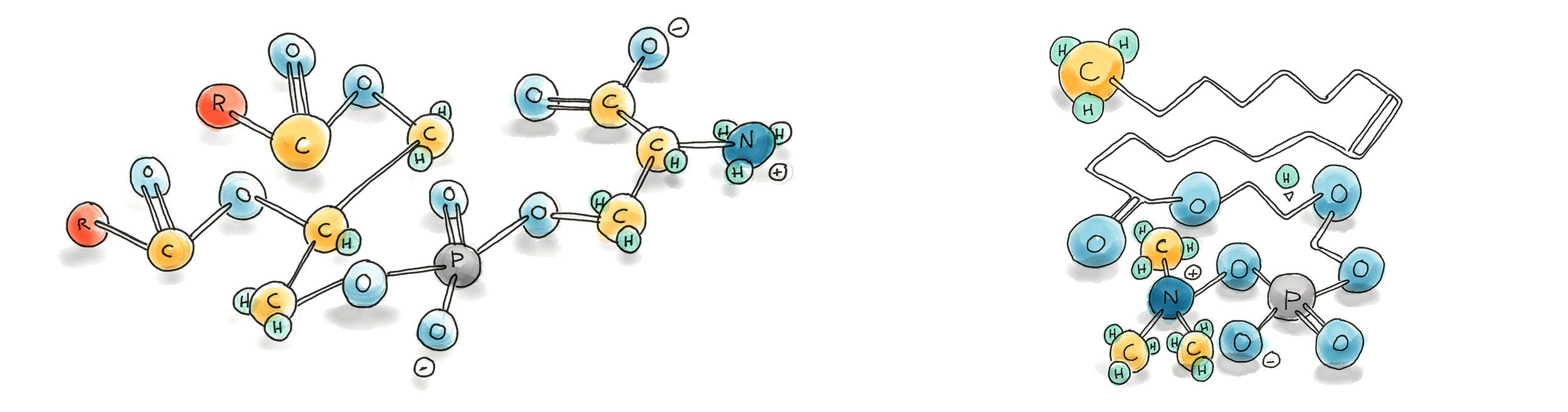
Both phosphatidylcholine (PC) and phosphatidylserine (PS) are essential phospholipids—fatty molecules that make up the structure of every cell membrane.
Phosphatidylserine (PS)
PS is concentrated in the inner layer of the cell membrane, especially in nerve and brain tissue. It’s crucial for cell signaling, neurotransmitter release, and healthy cognitive function. Supplemental PS is often used to support memory and cognitive performance.*
PS is not the most abundant phospholipid in the brain—phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) and phosphatidylcholine (PC) are more prevalent—but PS plays an outsized role in neuron communication and signaling.
Phosphatidylcholine (PC)
PC is the most abundant phospholipid in the body. It forms the outer layer of all cell membranes and is especially concentrated in liver, intestinal, and mitochondrial membranes.
PC is also the body’s primary source of choline, the nutrient used to make acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter essential for memory, focus, and muscle control.
Key Roles of Each
Phosphatidylserine (PS):
-
Concentrated in brain and nerve tissue
-
Regulates neurotransmitter release and signaling
-
Participates in cell growth and apoptosis (programmed cell renewal)
-
Supports healthy stress hormone balance (cortisol regulation)
Phosphatidylcholine (PC):
-
Structural backbone of all cell membranes
-
Supports liver detoxification and bile flow
-
Protects the intestinal lining and gut barrier integrity
-
Essential for mitochondrial energy and brain function
-
Provides choline for acetylcholine synthesis
The Relationship Between PC and PS
Your body can synthesize PS from PC or phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) through an enzyme-mediated “base exchange” process. This means that while PS isn’t present in BodyBio PC, adequate PC helps your body make the PS it needs naturally.
In other words, PC supports the production of PS, even though it doesn’t contain PS itself.
Because PC and PE are more abundant phospholipids, they act as the precursors or “parents” of PS. When the brain or other tissues require more PS—for example, during periods of cognitive demand or stress—the body can convert PC or PE into PS as needed.
The Case for Phosphatidylcholine Supplementation
Supplemental PC supports whole-body cellular function, including the brain. It’s the most efficient way to replenish phospholipids systemically, helping your body maintain the ideal balance and ratio of PC, PE, and PS over time.
Research-backed benefits of PC include:
-
Enhancing liver function and detoxification
-
Supporting healthy cholesterol transport and bile flow
-
Promoting brain and mitochondrial resilience
-
Strengthening the gut barrier by replenishing GI phospholipids
-
Providing choline for methylation and acetylcholine production
Because PC is the foundation of all membranes, it acts as a “mother molecule” from which other phospholipids, including PS, can be synthesized.
Why BodyBio PC Is Unique
While BodyBio PC does not contain phosphatidylserine, it provides a phospholipid complex rich in phosphatidylcholine, along with smaller amounts of phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) and phosphatidylinositol (PI). These phospholipids occur in their natural ratios, mirroring the composition of healthy human cells.
This allows your body to:
-
Rebuild and restore cell membranes systemically
-
Maintain proper lipid balance for brain, liver, and gut health
-
Endogenously produce PS and other phospholipids as needed
Decades of clinical use and research support the role of PC in restoring membrane integrity and optimizing cellular communication across systems.
Working Together for Cellular Health
If you’re debating whether to take phosphatidylserine or phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylcholine is the more foundational choice. It’s more abundant throughout the body, more versatile, and provides the building blocks to create PS naturally.
For comprehensive cellular support, a phospholipid complex like BodyBio PC helps maintain optimal membrane composition, empowering your body to make and regulate all its key phospholipids in balance.